The recent travel ban imposed by President Donald Trump has sparked widespread debate across the United States, with its effects on immigration, national security, and the economy drawing significant attention. While much of the public discourse has focused on the border policies targeting immigrants, the travel ban—upheld by the Supreme Court in a 5-to-4 decision—has also had far-reaching consequences that extend beyond the immediate political narrative.
What Does the Travel Ban Actually Do?
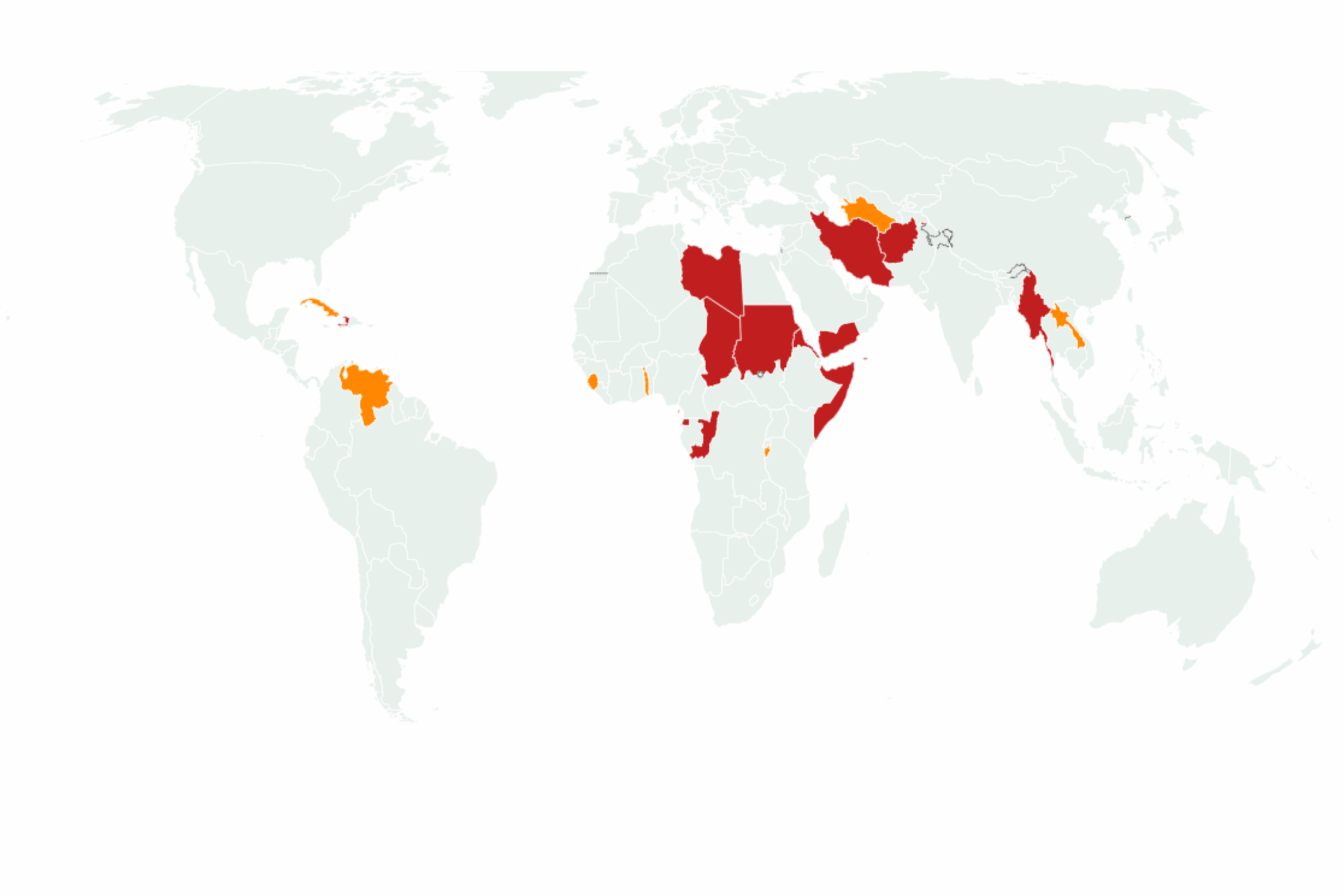
The travel ban, initially introduced as a presidential proclamation, targets individuals from seven countries with Muslim majorities—Libya, Iran, Somalia, Syria, and Yemen—as well as North Korea and Venezuela. It indefinitely suspends the issuance of both immigrant and nonimmigrant visas for applicants from these nations. This means that anyone seeking to enter the U.S. for work, study, or family reunification from these countries faces significant barriers.
In addition to the seven countries, the ban also imposes stricter visa requirements on seven other nations: Burundi, Cuba, Laos, Sierra Leone, Togo, Turkmenistan, and Venezuela. These restrictions vary depending on the individual’s purpose of travel, with some groups, such as wealthy businesspeople, potentially still allowed entry while others face more hurdles.
Why Did Trump Implement This Ban?

President Trump justified the travel ban by citing national security concerns, linking it to potential threats posed by individuals from the targeted countries. In a video released on social media, he referenced a terror attack in Boulder, Colorado, as a reason to tighten entry rules. However, critics argue that the selection of countries appears arbitrary, as none of the perpetrators of domestic terrorist attacks in the U.S. have come from the listed nations.
Furthermore, the administration claims that some of the affected countries do not provide sufficient information about their citizens, making it difficult to assess potential risks. Others point to the broader context of Trump’s rhetoric, noting that several of the countries on the list were previously labeled as “shithole countries” by the president during his first term.
Who Is Exempt From the Ban?

Despite the broad scope of the travel ban, there are several exemptions. These include:
- Individuals with Green Cards
- Dual citizens with U.S. passports
- Athletes and trainers participating in international competitions
- Afghan interpreters who worked with the U.S. military
- Iranian religious or ethnic minorities facing persecution
- Diplomats and UN officials
- Family members of U.S. citizens (spouses, children, parents)
- Adopted children of U.S. citizens
- Long-term foreign government employees (15 years or more)
These exemptions aim to mitigate the impact on certain vulnerable groups, though many argue that the overall effect of the ban is still severe.
The Economic and Social Impact
The travel ban has had significant economic and social consequences, particularly for small businesses and the hospitality industry. Many entrepreneurs and business owners rely on international visitors and immigrants to drive growth and innovation. For instance, Silicon Valley, known for its diverse workforce, has seen concerns that the ban could stifle the flow of talent and investment.
According to a 2017 report, over 40% of Fortune 500 companies were founded by immigrants or children of immigrants. These companies employ millions of Americans and contribute billions to the U.S. economy. The ban could deter future entrepreneurs, reducing the number of new businesses and jobs created.
Additionally, the hospitality sector, which includes hotels, restaurants, and tour operators, has faced challenges due to decreased tourism. With fewer international visitors, these small businesses may struggle to remain viable, especially in regions heavily dependent on tourism.
Reactions and Criticisms
The travel ban has drawn criticism from various sectors, including academia, human rights organizations, and international leaders. Harvard University, for example, faced specific scrutiny when Trump announced restrictions on international students, including those from the university. Critics argued that this move threatened the diversity and global perspective that institutions like Harvard bring to the U.S. education system.
Internationally, many countries expressed concern over the ban, with some calling it discriminatory and unjustified. Germany, for instance, criticized the policy as an attack on academic freedom and democracy, even suggesting that Harvard could establish an “exile campus” in Germany.
Conclusion
The travel ban represents a complex intersection of national security, economic interests, and humanitarian concerns. While the administration argues that it is necessary to protect the country from potential threats, critics highlight its negative impact on the economy, social fabric, and the principles of inclusivity that define the United States. As the debate continues, it remains to be seen how this policy will shape the future of immigration and international relations in the U.S.